Partitioning
Partitioning schemes can be confusing when installing Linux. I must admit i am very lazy when it comes to setting up a disk correctly. I have been spoiled with Fedora and Debian with their automatic partitioning systems, These are a couple of examples in partitioning a disk.
What is a Swap Partition and why would I use it?
Swap space in Linux is used when the amount of physical memory (RAM) is full. If the system needs more memory resources and the RAM is full, inactive pages in memory are moved to the swap space. While swap space can help machines with a small amount of RAM, it should not be considered a replacement for more RAM.
In this example I am going to show you how to partition a disk with Parted. Parted is quick and easy utility with great support for GPT partitions as well as MBR.
NOTE: I am using a VirtualBox with a 25GB partition. These examples should work fine for you.
UEFI/GPT example
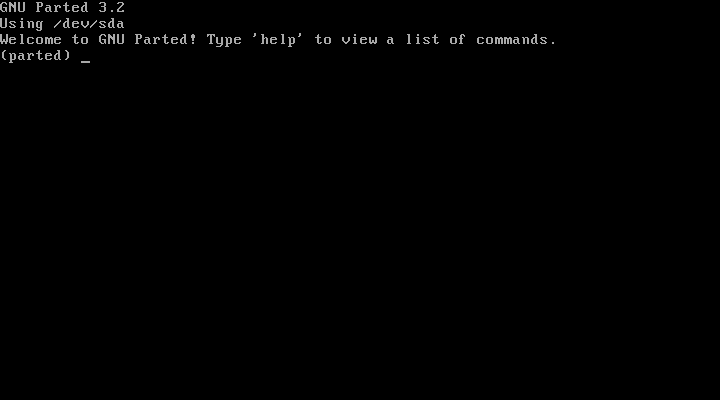
To start Parted: type parted /dev/sdx "sdx" being the name of your disk
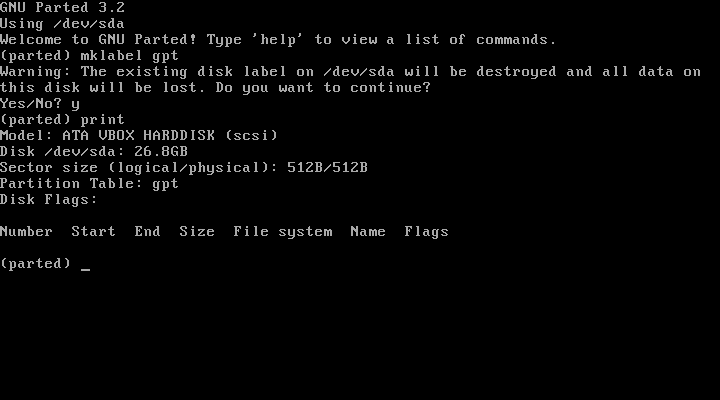
To create a new GPT partition table for UEFI systems instead, use:
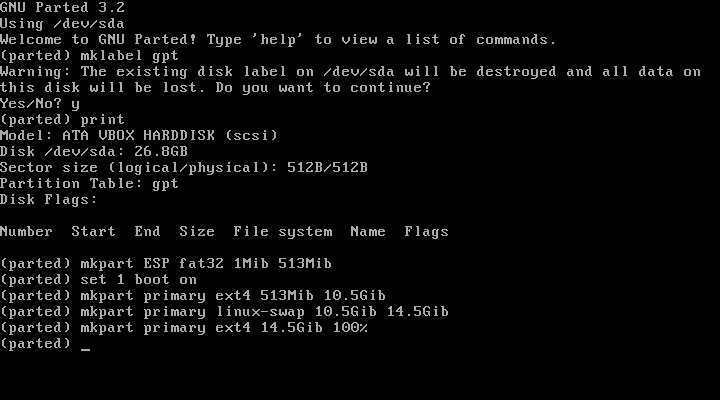
Type in order:
(parted) set 1 boot on
(parted) mkpart primary linux-swap 10.5GiB 14.5GiB
(parted) mkpart primary ext4 14.5GiB 100%
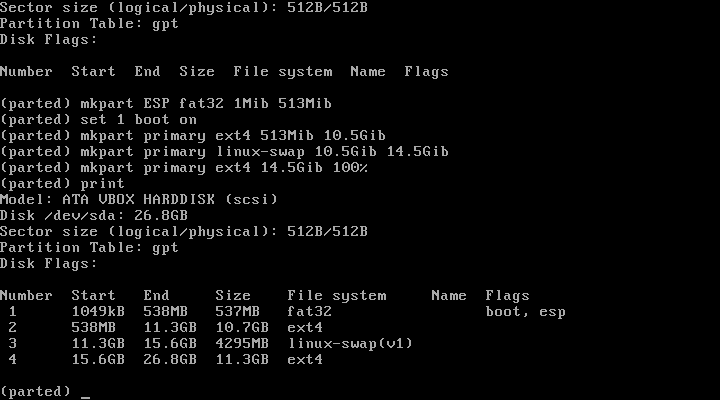
Now type print, This will display your partitions.
That's it your are now ready to install your linux of choice,
BIOS/MBR example
To start Parted: type parted /dev/sdx "sdx" being the name of your disk

To create a new MSDOS partition table for systems use:

Type in order:
(parted) set 1 boot on
(parted) mkpart primary linux-swap 10GiB 14GiB
(parted) mkpart primary ext4 14GiB 100%

Now type print, This will display your partitions.

That's it your are now ready to install your linux of choice,
Thank you for reading.